
The readout is only for the normal curve. When the Phase control is activated, the horizontal cross-hair line to the left of center represents the normal curve, the right side represents the phase curve. Place the mouse courser over the graph to activate the cross-hairs. The Response panel provides vertical and horizontal cross-hairs with a dynamic frequency and level read-out. Sets the size of the graphical Response graph: Small, Medium, Large. Response Panel: EnabledĮnables or disables the graphical Response graph. Sets the number of input/output channels for Multi-Channel, from 2 to 256. Multi-Channel enables the Count property. Sets the type of input/output channels: Mono, Stereo, or Multi-Channel.

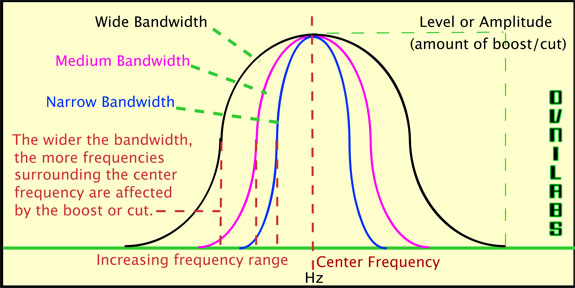
Note: The actual transition bandwidth can still be adjusted using the Lower and Upper Bandwidth controls in the control panel. If the default option (1/12 Octave) results in resource usage that is too high and if a wider transition bandwidth is acceptable, select a wider option. A wide (1 Octave) transition results in less computational resources being used while a narrow (1/12 Octave) transition results in more computational resources being used. Min Transition Bandwidthĭetermines how quickly the response transitions from the non-gain region to the gain region or vice versa. Sets the number of bands available in the Equalizer, from 1 to 32. The overall equalizer phase response is minimum-phase. Responses of adjacent bands with identical gains, transition bandwidths, and frequencies sum perfectly. This allows for flattop responses with asymmetrical slopes.

At the selected Frequency, the gain changes approximately +3dB or -3dB depending on whether the shelf is adding or reducing gain.īoth lower and upper transition bandwidths and frequencies can all be adjusted independently. Additionally, you can change any or all of the bands to either a high or low-shelf equalizer, allowing you to vary the gain of all frequencies, as a group, above or below a selected frequency.
Master controls, affecting all bands, include Bypass, Invert, Mute and Gain. It is a variable equalizer that allows you to individually adjust the Gain, Bandwidth, center Frequency, and lower and upper transition Bandwidths and Frequencies of up to 32 frequency bands. The Flattop Parametric Equalizer component is similar to the standard Parametric Equalizer, but offers asymmetrical filtering for more precision tuning of loudspeaker responses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
